Page 24 - 19BAR0028
P. 24
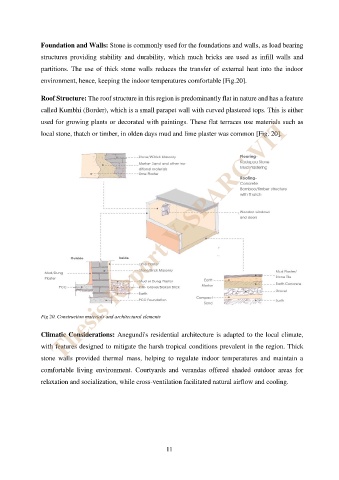
Foundation and Walls: Stone is commonly used for the foundations and walls, as load bearing
structures providing stability and durability, which much bricks are used as infill walls and
partitions. The use of thick stone walls reduces the transfer of external heat into the indoor
environment, hence, keeping the indoor temperatures comfortable [Fig.20].
Roof Structure: The roof structure in this region is predominantly flat in nature and has a feature
called Kumbhi (Border), which is a small parapet wall with curved plastered tops. This is either
used for growing plants or decorated with paintings. These flat terraces use materials such as
Thesis Report V-SPARC VIT
local stone, thatch or timber, in olden days mud and lime plaster was common [Fig. 20].
Fig 20. Construction materials and architectural elements
Climatic Considerations: Anegundi's residential architecture is adapted to the local climate,
with features designed to mitigate the harsh tropical conditions prevalent in the region. Thick
stone walls provided thermal mass, helping to regulate indoor temperatures and maintain a
comfortable living environment. Courtyards and verandas offered shaded outdoor areas for
relaxation and socialization, while cross-ventilation facilitated natural airflow and cooling.
11